Article posted on Mar 10, 2025
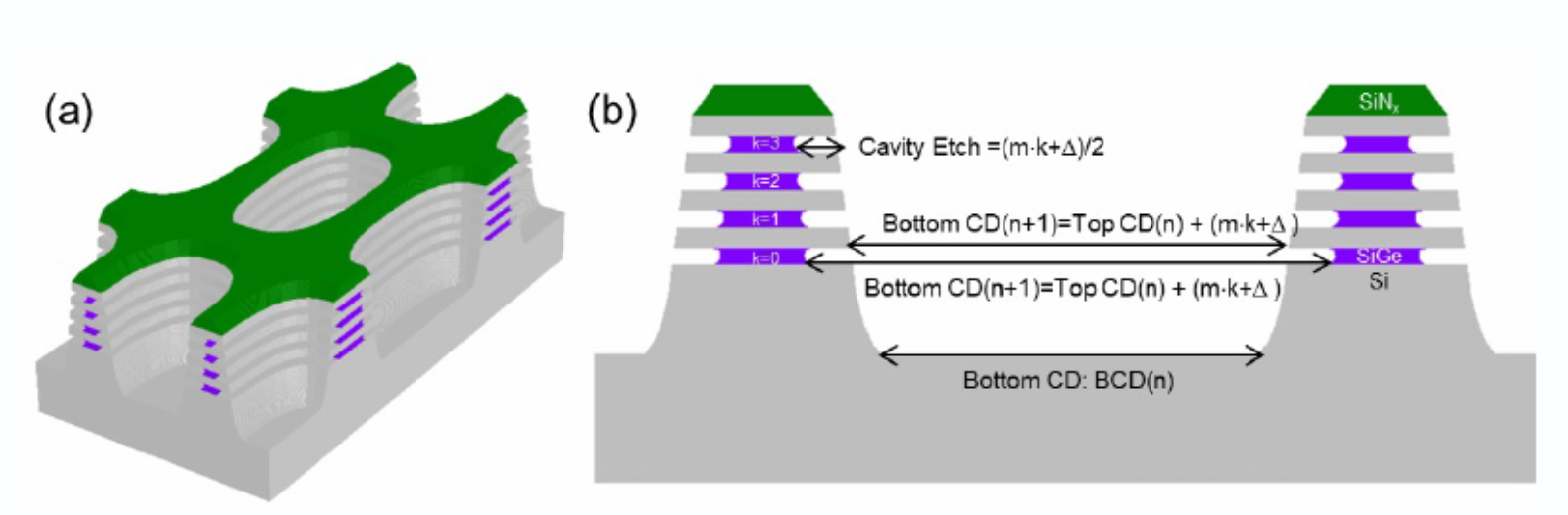

Optical critical dimension metrology (OCD), also known as optical scatterometry, has been an integral part of the semiconductor “critical dimension” process control ecosystem for over two decades. OCD has inherent advantages over competing measurement techniques (such as CD-SEM, AFM, and cross-sectional SEM) because it is noncontact, non-destructive, fast (sub-second acquisition time), and extremely precise. OCD is an indirect, model-based optical technique (typically spectroscopic) that allows for the extraction of critical geometric parameters, asymmetries, and optical properties of periodically patterned structures at sensitivities much less than the measurement wavelength of light (>100x smaller). Such sensitivity to multiple geometric parameters and material properties is due to the use of polarization-sensitive measurement techniques, like spectroscopic ellipsometry, and a sophisticated electromagnetic (EM) solver to simulate the spectral response of a periodic structure. If you already have a spectroscopic ellipsometer, you have the best way to measure thin film thicknesses and optical properties and a potential OCD tool to characterize 3D nanostructures. The missing piece is the analytical modeling software, which is where Ai Diffract, from Onto Innovation, comes in.