Picosecond Ultrasonics: An Advanced Technology Utilized for Process Control of SiCr Thin Film Resistors
Abstract
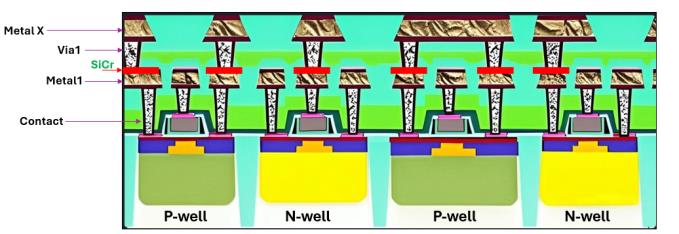
The bipolar-CMOS-DMOS (BCD) process is an advanced semiconductor technology integrating bipolar, CMOS, and DMOS devices onto a single chip, providing a compact, high-performance platform for the integration of analog, digital, and power circuitry. Thin-film resistors are employed to ensure precise resistance values and minimal temperature coefficients (TCR), thereby delivering enhanced accuracy and reliability for analog circuit applications. The SiCr thin-film resistor exhibits low TCR, consistent resistance values, minimal parasitic capacitance, and low leakage current. These characteristics surpass those of diffusion resistors, making SiCr thin-film resistor a good candidate for the precision resistance networks required in high-accuracy integrated and module circuits for BCD process. Picosecond ultrasonics (PULSE™ technology) has become a prevalent method in metal film measurement due to its rapid, contactless, and non-destructive capabilities. In this work, we demonstrate that picosecond ultrasonics has outstanding repeatability [1sigma<0.5Å] in SiCr thickness measurement as well as its excellent sensitivity to small thickness variations. SiCr thickness and uniformity could be well monitored and controlled. Furthermore, PULSE technology can reflect the surface quality of the film by measuring the probe beam (522nm) reflectivity. Then, specialty gases flow rate would be closely monitored and controlled to achieve target SiCr thin films with desirable TCR properties.
You Have a Challenge? Let’s talk.
We’d love to connect with you.
Looking to learn more about our innovative solutions and capabilities? Our team of experts is ready to assist you. Reach out today and let’s starts a conversation about how we can help you achieve your goals.
Let’s Talk
"*" indicates required fields